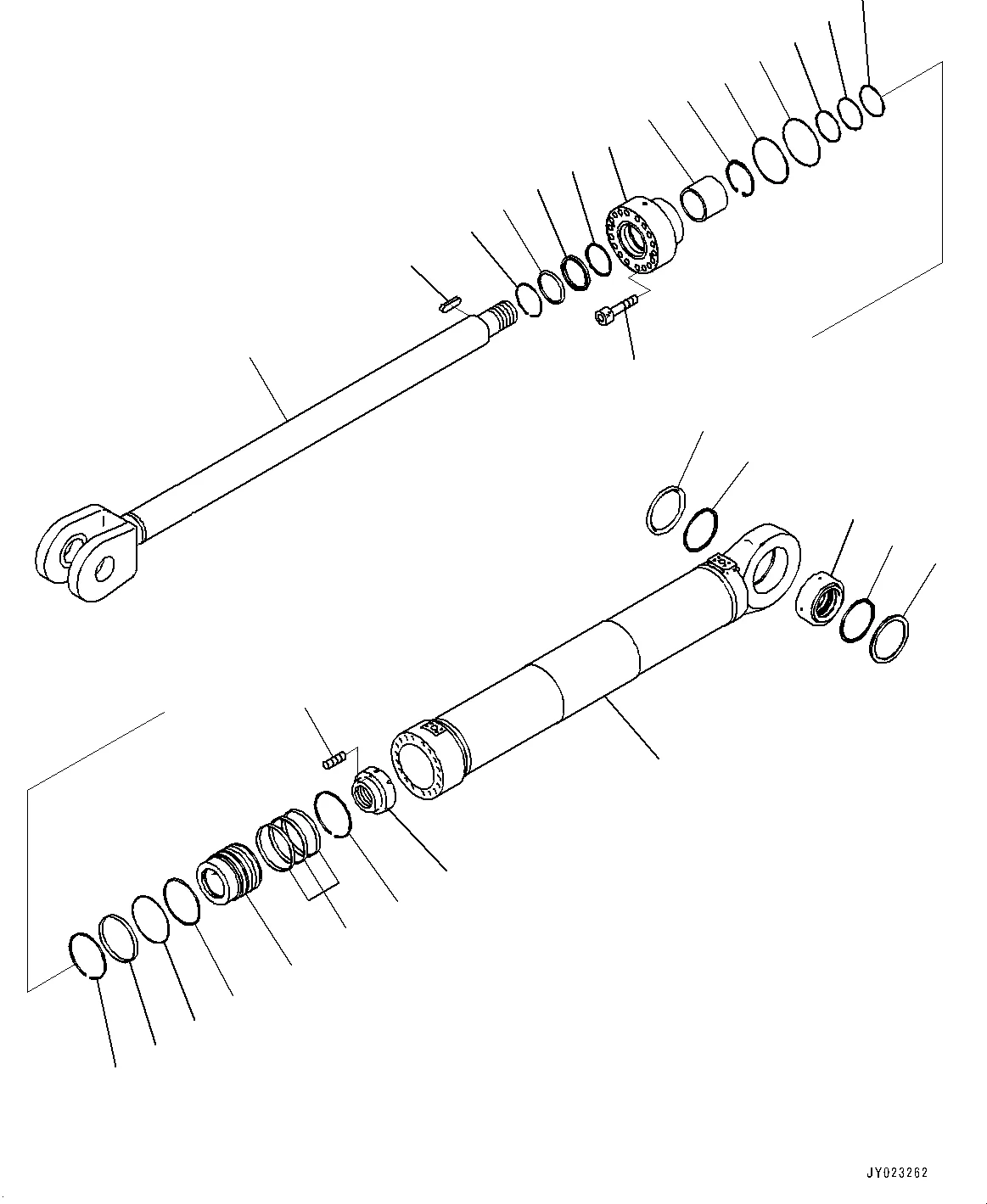
PRODUCTS
Hydraulic Cylinder Selection Simplified A Step by Step Approach
2025-06-25
Choosing the correct hydraulic cylinder can seem like a daunting task, since there are a wide range of sizes, configurations, and specifications available. But employing a system will make all of this a lot easier. Hydraulic Cylinder Selection Made Simple Step by Step is that guide and simplifies the process so that the engineers and technicians can know how to select a hydraulic cylinder. Instead of seeing it as browsing through a catalog, it goes beyond that by providing a methodology to ensure its functionality and endurance. The hydraulic systems have to function efficiently and reliably, for which it is important that one should know the various aspects of the cylinder selection. Understanding The Requirements Of The Application
While exploring technical specifications is important, gaining appreciation for the application comes first. This may involve ascertaining the load that needs to move, stroke length, speed of operation, and even how the actuator can be mounted to the intended device. Take into account the type of ambient environment in which the equipment would be operated, the duty cycle (continuous vs. intermittent), and the possibility of shock loads. A proper measurement of these features is the key to utilizing that cylinder selection process successfully.
Also, think about how the entire system is perceived. Does this application need a single-acting or double-acting cylinder? The working stroke of single-acting cylinders is pistons, operated by means of hydraulic pressure, the return uses gravity or a spring, while double-acting cylinders use hydraulic pressure for both extend and retract stroke. Your selection will largely depend upon your application requirements and the available real estate.
Selecting Cylinder Model and Mounting
Different types of hydraulic cylinders are tie-rod, welded cylinders, and mill-type cylinders. Tie-rod cylinders are economical and also provide some versatility, while welded cylinders have a stouter yet more compact configuration and are generally preferred for high-pressure applications. They are most commonly used in mill-type cylinders which tend to be larger and rugged. The decision is based on pressure needs, load limits, and environmental conditions.
The choice of mounting also has an effect on cylinder selection. Common types of mounting styles include clevis, flange, and trunnion mounts. Which depends on the angular constraints of the application and whether the cylinder axis has the normal orientation. Appropriate mounting is vital to ensuring alignment, stress distribution and minimizing the risk of premature failure plague.
Evaluating Cylinder Specs
For example, once the application requirements and cylinder type are established, attention focuses on things like bore size, rod diameter and pressure rating. As the bore size determines the output force of the cylinder, the rod diameter affects the bottom stroke end force. The pressure rating should be higher than the maximum operating pressure of the hydraulic system. Caution during this step and selection helps to avoid system errors and destruction.
Finally, do not forget about cushioning (to prevent shock loads at the end of the stroke) and seals (to keep the compressed air from leaking). The "Step-wise Method" teaches selecting suitable soft materials for the seal & cushion according to the character of the operating fluid plus the environment condition for the hydraulic cylinder's best operation and durability.
https://www.songteparts.com
While exploring technical specifications is important, gaining appreciation for the application comes first. This may involve ascertaining the load that needs to move, stroke length, speed of operation, and even how the actuator can be mounted to the intended device. Take into account the type of ambient environment in which the equipment would be operated, the duty cycle (continuous vs. intermittent), and the possibility of shock loads. A proper measurement of these features is the key to utilizing that cylinder selection process successfully.
Also, think about how the entire system is perceived. Does this application need a single-acting or double-acting cylinder? The working stroke of single-acting cylinders is pistons, operated by means of hydraulic pressure, the return uses gravity or a spring, while double-acting cylinders use hydraulic pressure for both extend and retract stroke. Your selection will largely depend upon your application requirements and the available real estate.
Selecting Cylinder Model and Mounting
Different types of hydraulic cylinders are tie-rod, welded cylinders, and mill-type cylinders. Tie-rod cylinders are economical and also provide some versatility, while welded cylinders have a stouter yet more compact configuration and are generally preferred for high-pressure applications. They are most commonly used in mill-type cylinders which tend to be larger and rugged. The decision is based on pressure needs, load limits, and environmental conditions.
The choice of mounting also has an effect on cylinder selection. Common types of mounting styles include clevis, flange, and trunnion mounts. Which depends on the angular constraints of the application and whether the cylinder axis has the normal orientation. Appropriate mounting is vital to ensuring alignment, stress distribution and minimizing the risk of premature failure plague.
Evaluating Cylinder Specs
For example, once the application requirements and cylinder type are established, attention focuses on things like bore size, rod diameter and pressure rating. As the bore size determines the output force of the cylinder, the rod diameter affects the bottom stroke end force. The pressure rating should be higher than the maximum operating pressure of the hydraulic system. Caution during this step and selection helps to avoid system errors and destruction.
Finally, do not forget about cushioning (to prevent shock loads at the end of the stroke) and seals (to keep the compressed air from leaking). The "Step-wise Method" teaches selecting suitable soft materials for the seal & cushion according to the character of the operating fluid plus the environment condition for the hydraulic cylinder's best operation and durability.
https://www.songteparts.com
Give Us What You Need
Ready to learn more? Fill out the form and a member of our dedicated team will reach out to you promptly!
We will contact you within 24 hours after receiving the information
SUBSCRIBE
INQUIRY
_5t33iQdr.png)