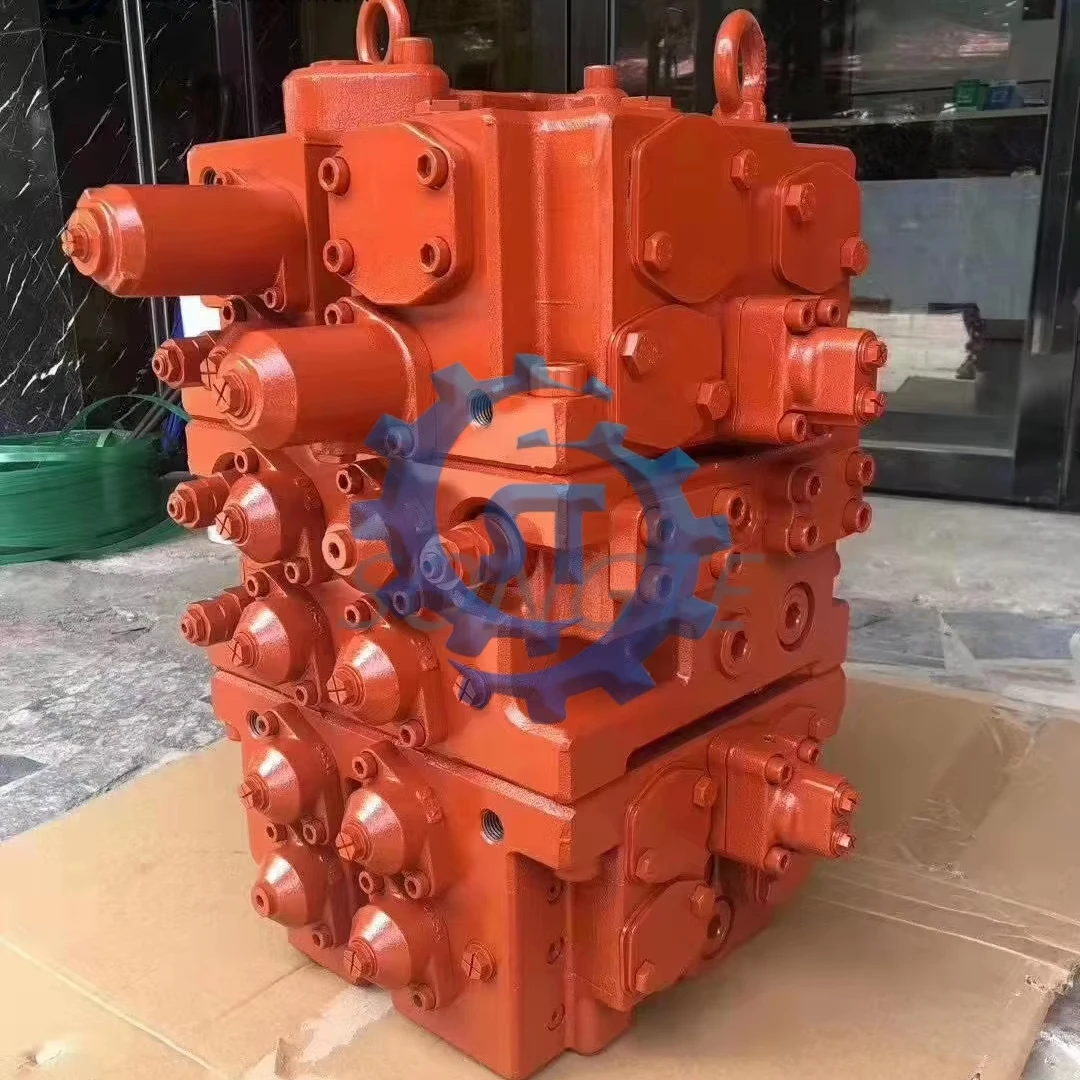
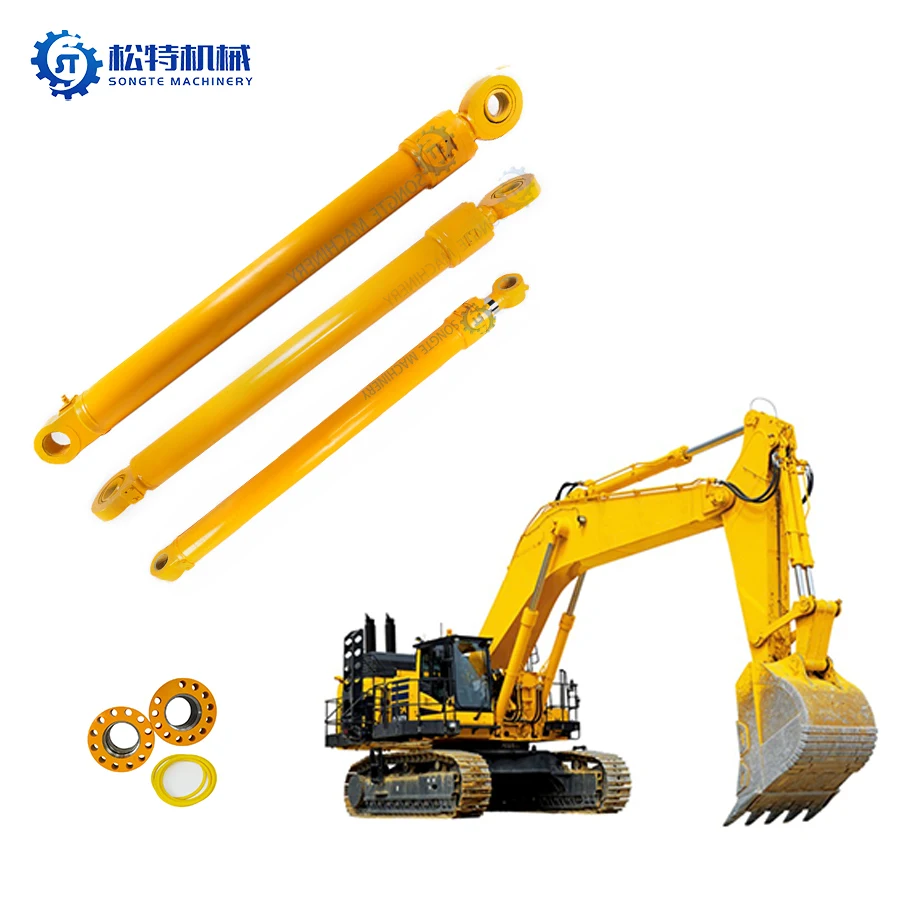
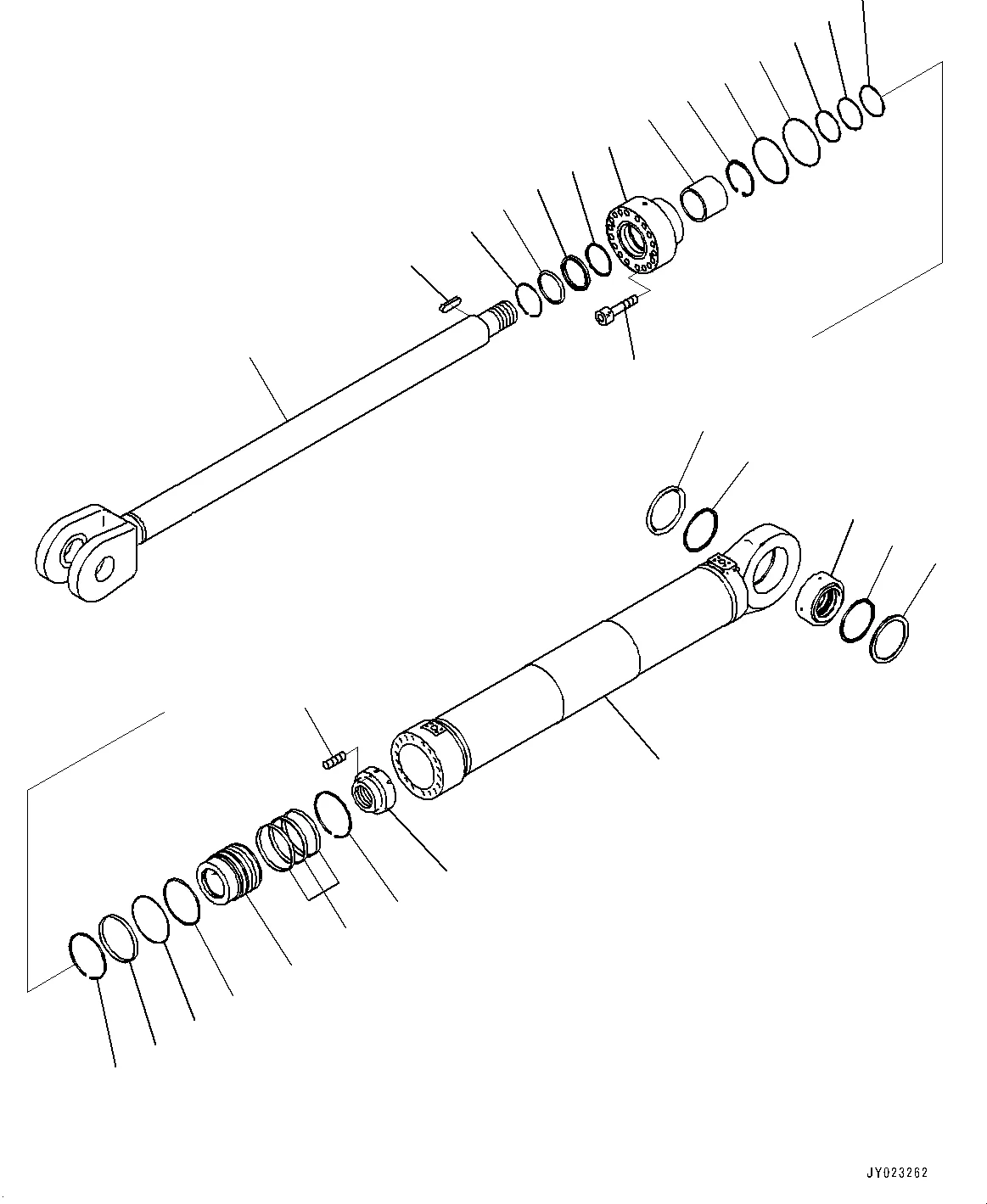
PRODUCTS
Mastering Hydraulic Cylinder Selection Key Factors and Considerations
2025-06-30
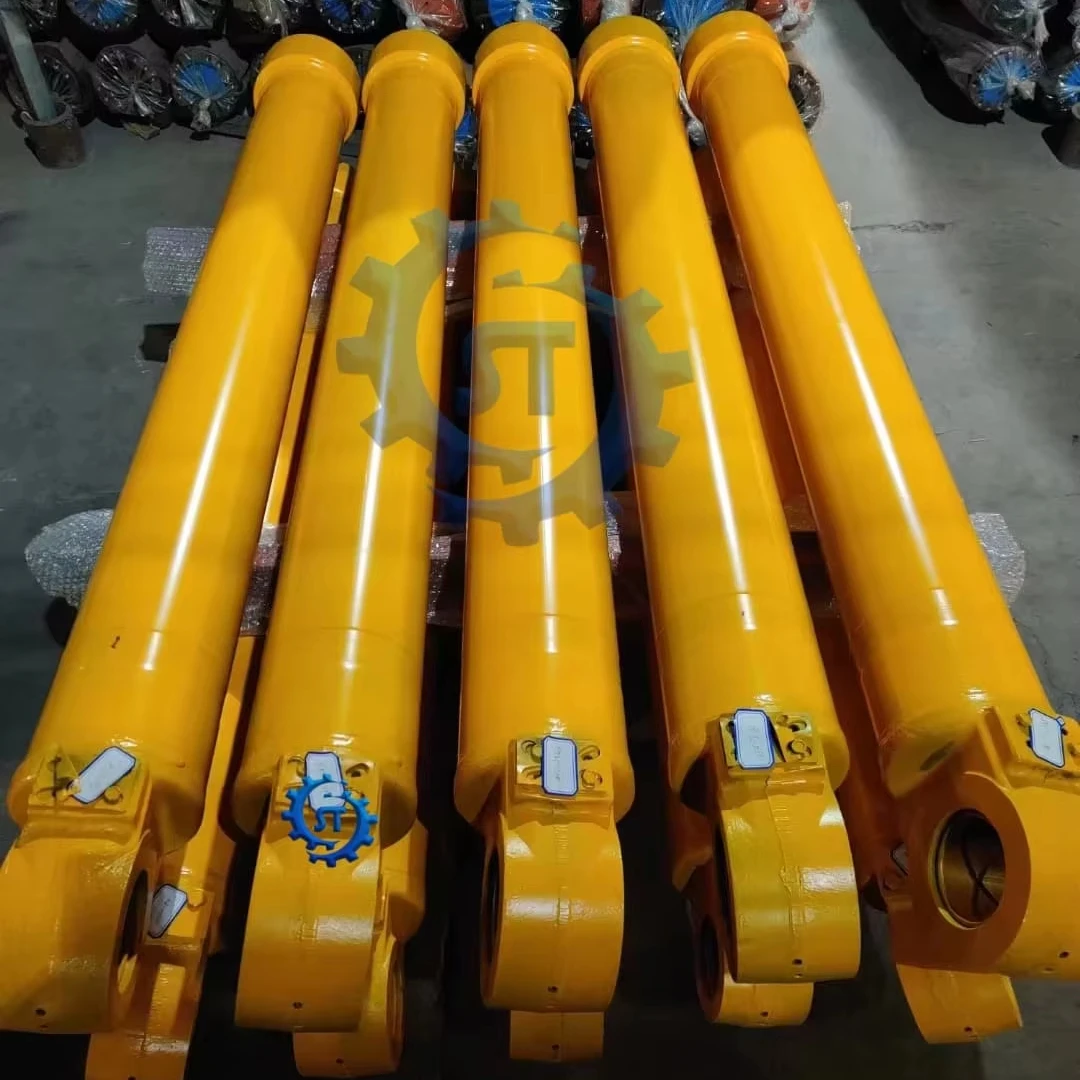
The proper selection of a hydraulic cylinder is critical for the successful operation of any hydraulic system. Ill-suited cylinder components, can cause inefficiencies, shorten start and run lives, or in worse-case scenarios, cause failures. In this article, we have discussed the main aspects and consideration for mastering the selection of hydraulic cylinders for high performance and service life. Hydraulics and the terminology behind hydraulics is crucial for engineers, designers, and anyone near hydraulic systems. Bore Size and Rod Diameter
The bore diameter controls how much force the cylinder will produce and how big the rod diameter, impacts the force on retraction. Core bore sizes deliver more force but are made from larger components, which can drive up cost. The diameter of the rod is also a function of the retraction force required but also the potential for bending or buckling in compression. The transport capacity relates to the section to which power supply should be distributed, while the overall system design is limited by high current and high magnetic field approaches.
If you pick the bore or rod the wrong size, you either won't get enough force out of it for your application, or it will wear out way too soon. This is a sensitive decision where a need for detailed load calculations and safety factor consideration is necessary.
Stroke Length and Type of Mounting
Stroke length indicates how far the piston moves. Measuring the required travel would be most critical. Selecting a cylinder with too short a stroke will make the system incapable. And an overly sized stroke will take up space and create more expense.
The style by which it mounts will have a broad impact on the design and installation. These are addressed in various styles which include clevis, flange, trunnion, and eye mounts. Each provides distinct benefits depending on the force and geometry needed for the application. The right choice needs to be established so that the cylinder does not get unnecessary pressure and remains stable.
Type of fluid and Operating Pressure
This pressure has a major impact on the force that the cylinder can output. For the same force smaller cylinders can be used at higher pressure but more risk of component failure if not designed properly. It is important to choose it according to the maximum pressure the cylinder can bear.
The choice of hydraulic fluid directly influences seal lifetime and overall efficiency of the system. The viscosity, temperature range, and material compatibility requirements of the fluid need to be thoroughly analyzed; Choosing a wrong fluid could cause a seal to wear out quickly and the system fail.
Choice of Raw Materials and Environmental Aspects
The cylinder material needs to be compatible with the operating environment and loads expected. Material selection depends on various factors such as the required corrosion resistance, extreme temperature and exposure to chemicals. Taking stainless steel for an example, it provides great corrosion resistance but its cost will be higher than other materials.
Other cylinder life and performance implications may include cylinder wear due to environmental conditions, or dust, debris and moisture. Protective coatings or seals may be required, depending on the working conditions. Neglect of ambient conditions can lead to field failure and increased lifetime costs.
https://www.songteparts.com
The bore diameter controls how much force the cylinder will produce and how big the rod diameter, impacts the force on retraction. Core bore sizes deliver more force but are made from larger components, which can drive up cost. The diameter of the rod is also a function of the retraction force required but also the potential for bending or buckling in compression. The transport capacity relates to the section to which power supply should be distributed, while the overall system design is limited by high current and high magnetic field approaches.
If you pick the bore or rod the wrong size, you either won't get enough force out of it for your application, or it will wear out way too soon. This is a sensitive decision where a need for detailed load calculations and safety factor consideration is necessary.
Stroke Length and Type of Mounting
Stroke length indicates how far the piston moves. Measuring the required travel would be most critical. Selecting a cylinder with too short a stroke will make the system incapable. And an overly sized stroke will take up space and create more expense.
The style by which it mounts will have a broad impact on the design and installation. These are addressed in various styles which include clevis, flange, trunnion, and eye mounts. Each provides distinct benefits depending on the force and geometry needed for the application. The right choice needs to be established so that the cylinder does not get unnecessary pressure and remains stable.
Type of fluid and Operating Pressure
This pressure has a major impact on the force that the cylinder can output. For the same force smaller cylinders can be used at higher pressure but more risk of component failure if not designed properly. It is important to choose it according to the maximum pressure the cylinder can bear.
The choice of hydraulic fluid directly influences seal lifetime and overall efficiency of the system. The viscosity, temperature range, and material compatibility requirements of the fluid need to be thoroughly analyzed; Choosing a wrong fluid could cause a seal to wear out quickly and the system fail.
Choice of Raw Materials and Environmental Aspects
The cylinder material needs to be compatible with the operating environment and loads expected. Material selection depends on various factors such as the required corrosion resistance, extreme temperature and exposure to chemicals. Taking stainless steel for an example, it provides great corrosion resistance but its cost will be higher than other materials.
Other cylinder life and performance implications may include cylinder wear due to environmental conditions, or dust, debris and moisture. Protective coatings or seals may be required, depending on the working conditions. Neglect of ambient conditions can lead to field failure and increased lifetime costs.
https://www.songteparts.com
Give Us What You Need
Ready to learn more? Fill out the form and a member of our dedicated team will reach out to you promptly!
We will contact you within 24 hours after receiving the information
SUBSCRIBE
INQUIRY
_5t33iQdr.png)